PCR Blockers
PNA clamping is a technique that uses peptide nucleic acid (PNA) oligomers in PCR or hybridization assays to selectively suppress amplification or detection of unwanted DNA sequences. It is particularly effective for reducing amplification of wild-type DNA when detecting rare SNP mutations or minimizing background from host DNA, such as chloroplast or mitochondrial 16S rRNA, thereby enhancing the sensitivity of low-abundance microbial target detection. Another example is globin reduction using PNA. A blend of PNAs targeting human gamma globin RNA can suppress globin mRNA amplification during cDNA synthesis, leading to more diverse cDNA libraries for microarray analysis.
Due to its high affinity and specificity, PNA binds tightly to complementary sequences—even with minimal mismatches—and blocks access to primers without being extended by DNA polymerase, making it a highly effective molecular clamp. PNA clamping is effective correcting amplification bias and reduce sequencing errors.
Applications of PNA Clamping
- SNP and mutation detection
- Microbial profiling
- Rare allele enrichment
- Prey analysis
- PCR assays with high host DNA contamination
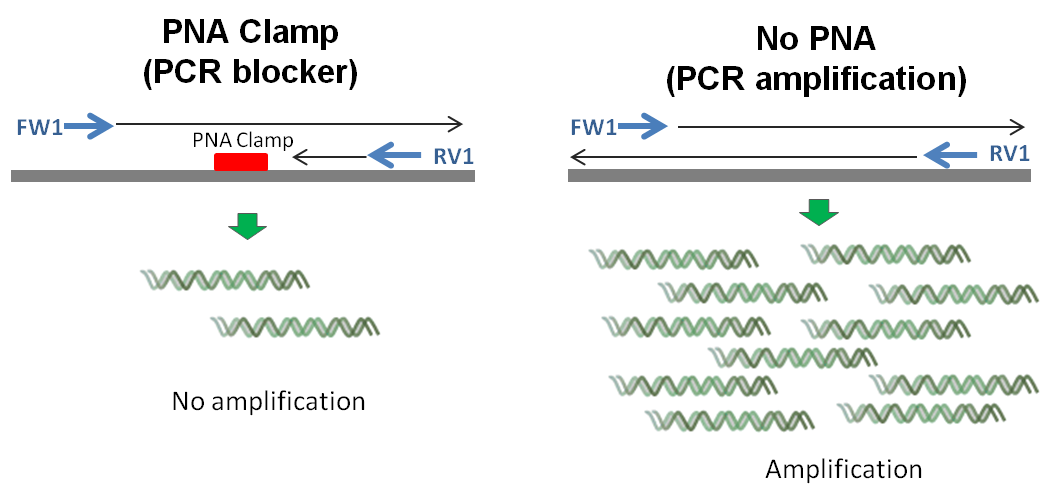
We offer catalog PNA clamps targeting plant mitochondrial and chloroplast as well as human globin sequences. For other applications, our team can assist with custom design and synthesis of PNA clamps tailored to your project. Please contact us at info@pnabio.com for more information.
PNA Clamps for Host DNA Suppression in Metagenomic Studies
16S, 18S, and 28S rRNA sequencing are widely used for taxonomic classification in metagenomics. However, a frequent challenge is host-derived contamination, where the majority of sequencing reads originate from the host’s mitochondrial or plastid genomes. This can obscure the detection of low-abundance microbial taxa.
To address this, PNA clamps (PNA PCR blockers) are designed to selectively bind to host rRNA regions, suppressing their amplification and enriching microbial sequences in your dataset.
🔬 PNA PCR Blockers We Offer
Our catalog includes a range of PNA blockers targeting mitochondrial, chloroplast, and ITS DNA from multiple host species.
| Product | Cat No | Sequence | Target | Available Sizes |
| mPNA | MP01-25/MP01-50 | GGCAAGTGTTCTTCGGA | mitochondria | 25 nmole & 50 nmole |
| pPNA | PP01-25/PP01-50 | GGCTCAACCCTGGACAG | chloroplast | 25 nmole & 50 nmole |
| Pop mPNA | PMP01-25 | GGCAAGTCTTCTTCGGA | mitochondria | 25 nmole |
| Quercus mPNA | QMP01-25 | KK-GTGAATTGGTTTCGAGA | mitochondria | 25 nmole |
| Asteraceae pPNA | APP01-25 | GGCTCAACTCTGGACAG | chloroplast | 25 nmole |
| ITS PNA | IP01-25/IP01-50 | CGAGGGCACGTCTGCCTGG | ITS2 | 25 nmole & 50 nmole |
All products are usually in stock and available for same-day shipping for next-day delivery.
🧪 How to Use PNA PCR Blockers
- Add PNA blockers directly to the PCR mix at a final concentration of 0.5 µM to 6 µM. Temperature: 70°C – 80°C
- Include a PNA clamping step between denaturation and primer annealing.
- For optimization, tryrange of clamping temperature to 65°C–80°C (about 10°C below to 5°C above the predicted Tm of the PNA).
- Duration: 10 – 30 seconds
- Add PNA blockers directly to the PCR mix.
🧬 Need a Custom Clamp?
If your host genome is not covered by the above options, we can design and synthesize a custom PNA clamp tailored to your target sequence.
📧 Contact us at info@pnabio.com for assistance, or visit our Custom PNA Oligos page for more information.
📚 Scientific References
- Practical innovations for high-throughput amplicon sequencing. Lundberg DS et al. (2013) Nat Methods 10:999-1002 (mPNA and pPNA)
- The Populus holobiont: dissecting the effects of plant niches and genotype on the microbiome. Cregger MA et al. (2018) Microbiome 6:31 (Populus mPNA and ITS PNA)
- Chloroplast sequence variation and the efficacy of peptide nucleic acids for blocking host amplification in plant microbiome studies. Fitzpatrick CR et al. (2018) Microbiome 6: 144 (Asteraceae pPNA)
- Peptide nucleic acid (PNA) clamps reduce amplification of host chloroplast and mitochondria rRNA gene sequences and increase detected diversity in 16S rRNA gene profiling analysis of oak-associated microbiota. Hussain U et al. (2025) Environmental Microbiome 20:14 (Quercus mPNA)
PNA Clamp to Suppress Aberrant Vk Transcript
🧬 Overview
A validated PNA clamp that selectively suppresses amplification of the aberrant MOPC-21–derived Vκ transcript in SP2/0- or P3X63Ag8.653-based hybridomas, enabling clean amplification of the functional light-chain Vκ from your hybridoma cDNA.
🧾 Product details
- Target: MOPC-21 aberrant Vκ (CDR3 region)
- PNA sequence (antisense to abVκ CDR3): 5’ CGTGTAAGCTCCCTA
- Validated use: PNA-mediated PCR clamping to prevent abVκ amplification while preserving amplification of functional hybridoma Vκ. In the cited work, PNA clamping eliminated abVκ clones and enriched functional Vκ clones.
🧪 PCR clamping conditions
⚗️ PCR Reaction Mix
- Primers (e.g., Vκ2Back/Vκ4For): 0.25 µM each
- PNA clamp: 2.5~10 µM
- Template: cDNA from hybridoma
- Volume: 20–50 µL
⏱️ PCR Cycle
- 94 °C, 2 min
- 30 cycles of:
- 94 °C, 20 s (denaturation)
- 65 °C, 30 s (PNA preferential clamping)
- 50 °C, 30 s (primer annealing)
- 60 °C, 30 s (extension)
- 60 °C, 2 min (final extension)
Globin mRNA is a majority of total mRNA in blood cells (over 70%) and can potentially reduce the sensitivity of non-globin mRNA.
Globin Reduction PNA is a novel, non-enzymatic technology that removes the majority of alpha and beta globin mRNA from total RNA preparations derived from whole blood. PNA oligomers can be effectively used as a clamp by specifically blocking globin mRNA during the process of reverse transcription and resulting in specific PCR amplification of the target non-globin mRNA for your analysis.
The 3 nmole kit (G2000-3) contains 3 nmole of each PNA and includes sufficient reagents for 250 reactions of 5 ug RNA preps. The larger size G2000-10 contains 10 nmole of each PNA.
Download protocol for Globin Reduction PNA Kit.
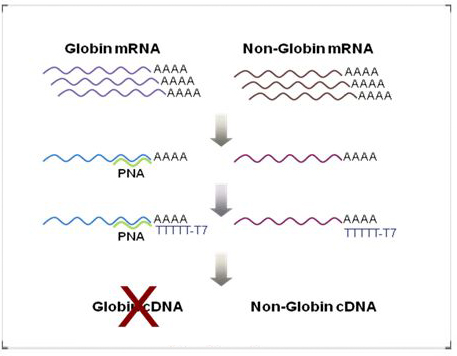
Globin reduction PNA is composed of the following 4 PNAs that are specific to alpha and beta globin mRNA. It works for both human and mouse globin mRNA.
- The sequences of G2001, GR PNA-L;
PNA1: k-TAA CGG TAT TTG GAG-k
PNA2: k-GTA GTT GGA CTT AGG-k
PNA3: k-GCC CTT CAT AAT ATC-k
PNA4: k-ATC CAG ATG CTC AAG-k
- The Populus holobiont: dissecting the effects of plant niches and genotype on the microbiome. Cregger MA et al. (2018) Microbiome 6:31.
- Chloroplast sequence variation and the efficacy of peptide nucleic acids for blocking host amplification in plant microbiome studies. Fitzpatrick CR et al. (2018) Microbiome 6:144.
- Practical innovations for high-throughput amplicon sequencing. Lundberg DS et al. (2013) Nat Methods 10:999 -1002.
- Identifying the plant-associated microbiome across aquatic and terrestrial environments: the effects of amplification method on taxa discovery. Jackerel SL et al (2017) Molecular Ecology Resources 1755-0998.12645.
- Application of Peptide Nucleic Acid-based Assays Toward Detection of Somatic Mosaicism. Hong CS et al (2016) Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 5(4): e314.
- DNA Clutch Probes for Circulating Tumor DNA Analysis. Das J et al. (2016) J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138 (34):11009–11016.
- Diagnostics based on nucleic acid sequence variant profiling: PCR, hybridization, and NGS approaches. Khodakov D et al. (2016) Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 105(Pt A):3-19.
- Rapid Intraoperative Molecular Characterization of Glioma. Shankar GM et al. (2015) JAMA Oncol. 1(5):662-667.
- Fractal circuit sensors enable rapid quantification of biomarkers for donor lung assessment for transplantation. Sage AT. (2015) Sci Adv. 1(7):e1500417.
- Increasing gene discovery and coverage using RNA-seq of globin RNA reduced porcine blood samples. Choi I et al (2014) BMC Genomics. 15:954.
- Peptide nucleic acid clamp PCR: a novel K-ras mutation detection assay for colorectal cancer micrometastases in lymph nodes. Taback B et al. (2004) Int J Cancer. 111(3):409-14.
- Single base pair mutation analysis by PNA directed PCR clamping. Orum H et al (1993) Nuc Acids Res 21(23):5332-5336.
- Efficiency of peptide nucleic acid-directed PCR clamping and its application in the investigation of natural diets of the Japanese eel Leptocephali. Terahara T et al (2011) pLOS One 6(11):e25715.
- High-sensitivity detection of the A3243G mutation of mitochondrial DNA by a combination of allele-specific PCR and peptide nucleic acid-directed PCR clamping. Urata M et al (2004) Clin Chem 50 (11)2045-2051.
- Use of a PNA probe to block DNA-mediated PCR product formation in prokaryotic RT-PCR. Bender M et al (2007) Biotechniques 42(5):609-1.
You can download the protocol for mPNA/pPNA
| Cat No | Item | Description | Size | Price | Order |
| MP01-25 | mPNA-S | Mitochondria rRNA blocker (ggcaagtgttcttcgga) | 25 nmole | $395.00 | Add to cart |
| MP01-50 | mPNA-L | Mitochondria rRNA blocker (ggcaagtgttcttcgga) | 50 nmole | $550.00 | Add to cart |
| PP01-25 | pPNA-S | Chloroplast rRNA blocker (ggctcaaccctggacag) | 25 nmole | $395.00 | Add to cart |
| PP01-50 | pPNA-L | Chloroplast rRNA blocker (ggctcaaccctggacag) | 50 nmole | $550.00 | Add to cart |
| IP01-25 | ITS-PNA-S | ITS rRNA blocker (cgagggcacgtctgcctgg) | 25 nmole | $425.00 | Add to cart |
| IP01-50 | ITS-PNA-L | ITS rRNA blocker (cgagggcacgtctgcctgg) | 50 nmole | $585.00 | Add to cart |
| APP01-25 | Asteraceae pPNA | Asteraceae chloroplast rRNA blocker (ggctcaactctggacag) | 25 nmole | $395.00 | Add to cart |
| PMP01-25 | Pop mPNA | Mitochondria rRNA blocker variant (ggcaagtcttcttcgga) | 25 nmole | $395.00 | Add to cart |
| QMP01-25 | Quercus mPNA | Oak mitochondria rRNA blocker (KK-gtgaattggtttcgaga) | 25 nmole | $415.00 | Add to cart |
| G2001-3 | GR PNA-S | A set of 4 PNA oligos against human globin | 3 nmole | $495.00 | Add to cart |
| G2001-10 | GR PNA-L | A set of 4 PNA oligos against human globin | 10 nmole | $1150.00 | Add to cart |
| VKP-01 | Vk PNA | Aberrant Vk PNA Blocker (cgtgtaagctcccta) | 50 nmole | $510.00 | Add to cart |