PNA FISH Probes
PNA Bio provides a range of catalog probes, including telomere, centromere, and CAG repeat probes. They can be used for cells or tissue sections. For other targets such as microorganisms or gene specific probes, we offer them as custom PNA. please visit our Custom PNA Oligos page for more information.
PNA FISH probes can also be designed as molecular beacons, functioning similarly to DNA molecular beacons. In the unbound state, the flexible and unstructured PNA backbone keeps the fluorophore and quencher in close proximity, effectively quenching fluorescence. When the probe hybridizes to its complementary DNA or RNA target, the structural change separates the fluorophore and quencher, resulting in a fluorescent signal.
Unlike DNA-based beacons, PNA molecular beacons do not require a stem-loop structure, simplifying probe design and enabling the use of shorter sequences. Combined with PNA’s high binding affinity, specificity, and chemical stability, these MB probes are ideal for real-time detection, mutation analysis, live-cell imaging, and clinical diagnostics.
For the recommended PNA FISH protocol, please download the following file.
If you would like assistance designing a PNA FISH probe specific to your target, please feel free to contact us
PNA FISH Probes and Reagents
PNA Bio offers a range of high-quality PNA FISH probes and buffers to support your fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) workflows. Our product line includes telomere, centromere, and DM1 repeat probes, along with optimized Hybridization and Blocking Buffers to streamline your experiments.
Our FISH probes and reagents are usually in stock and ship the same day if the order is received by 5 pm ET.
🧬PNA FISH Reagents
- PFB01: PNA FISH Hybridization Buffer (20 mM Tris, 60% formamide, pH 7.4 final), 30 ml
- PFB05: PNA FISH Blocking Buffer, 1.5 ml
🔬 Telomere PNA FISH Probes
We provide two telomeric probes for detecting repetitive sequences at chromosome ends:
- TelC (C-rich): Binds the leading strand containing 3 repeats of TAACCC
- TelG (G-rich): Binds the lagging strand containing 3 repeats of TTAGGG
These probes are compatible with human, mouse, rat, and most vertebrate chromosomes.
🧬 Centromere PNA FISH Probes
- CENPB Probe: Targets the CENP-B binding site
Sequence: ATTCGTTGGAAACGGGA
Stains all human and mouse centromeres except the Y chromosome - CENT Probe: Targets the human alpha satellite sequence
Sequence: AAACTAGACAGAAGCAT
Selectively stains human centromeres; not compatible with mouse chromosomes, and hybridization intensity may vary by chromosome
🧬 DM1 (CAG Repeat) PNA Probe
Our CAG repeat probe is designed to detect expanded CTG/CAG repeats in the DMPK gene, associated with Myotonic Dystrophy type 1 (DM1).
🧪 Sample Compatibility
- FFPE tissues
- Fixed cell preparations
🎨 Custom Fluorophores & Sequences
If you require a different fluorophore than those listed, please contact us at order@pnabio.com
For gene-specific targets not listed above, please visit our Custom PNA Oligos page.
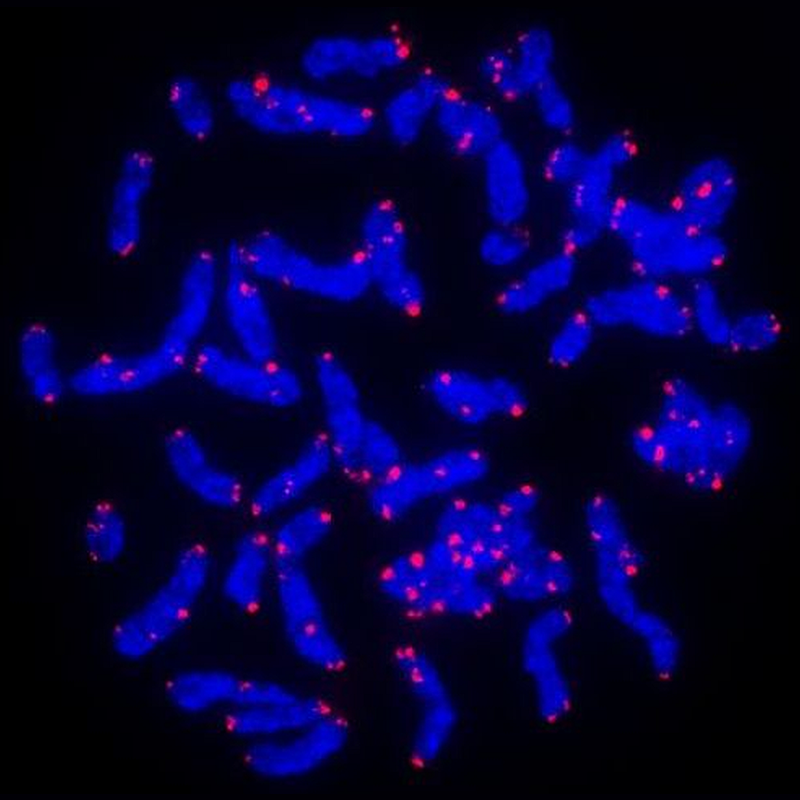 |
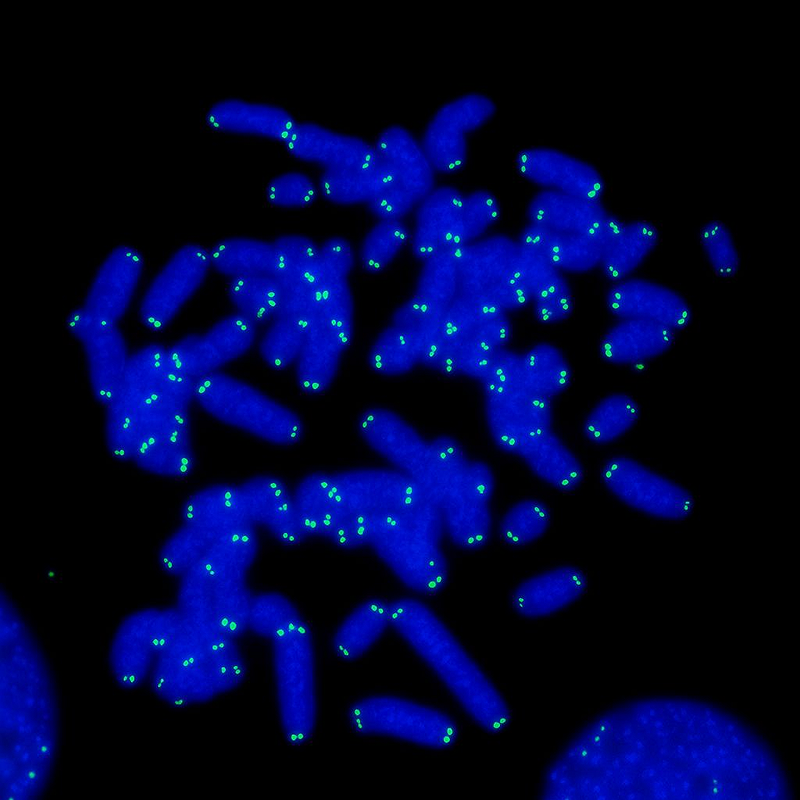 |
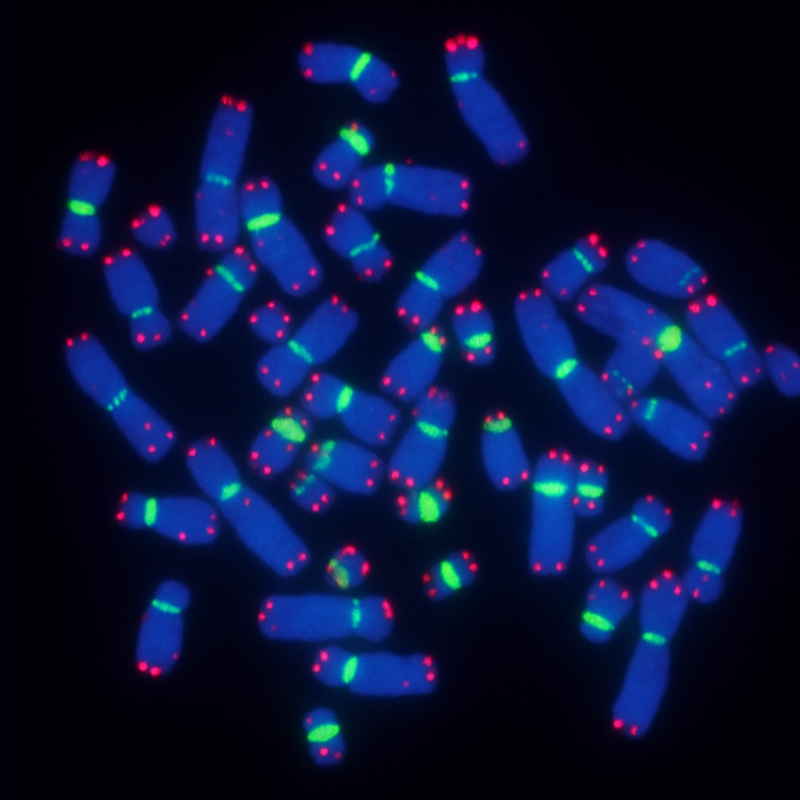 |
| F1002 (TelC-Cy3) | F1008 (TelG-A488) | F1002 & F3001 |
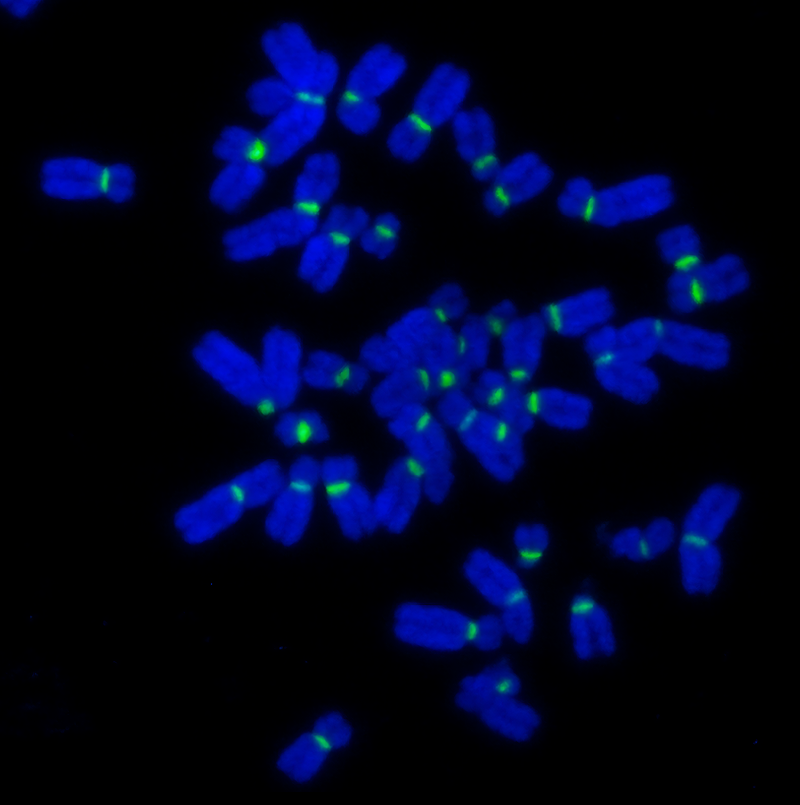 |
 |
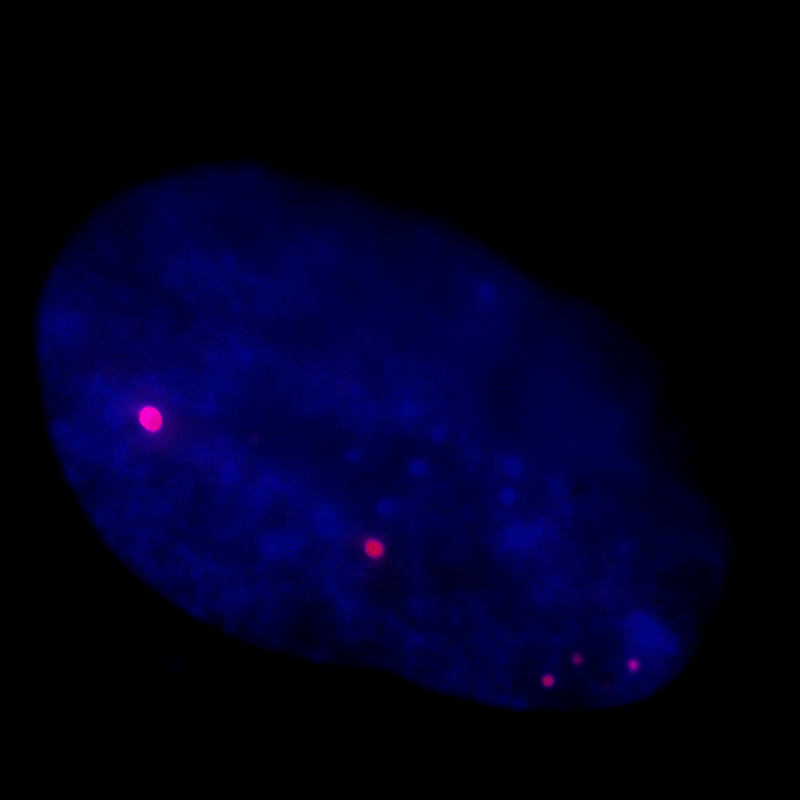 |
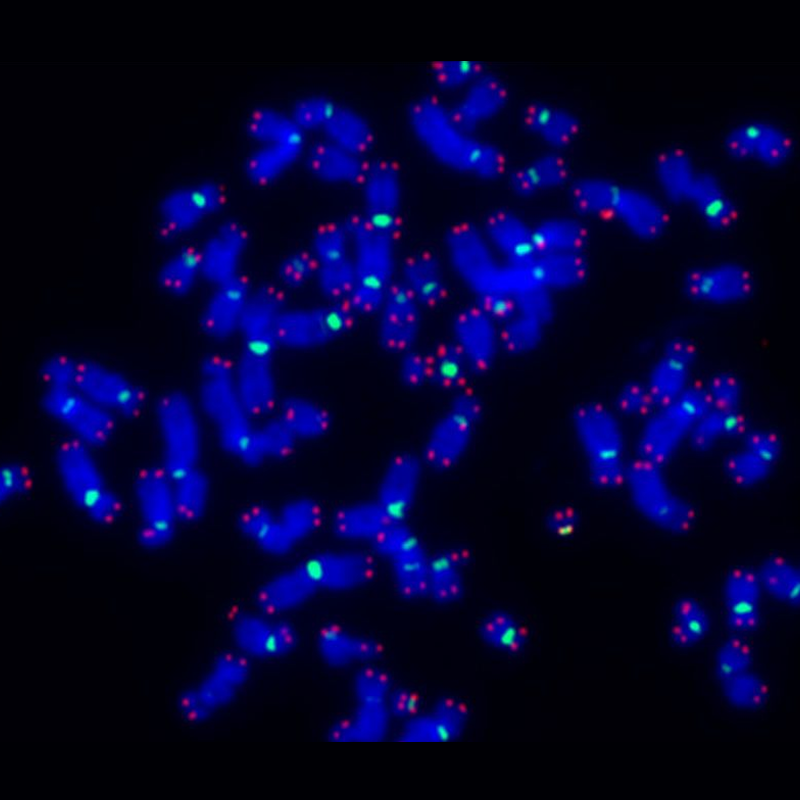
| F3004 (CENPB-A488) | F1006 & F3006 | F5001 (CAG-Cy3) |
| Catalog Number | Item | Label | Information |
| F1001 | TelC-FAM | FAM | TelC telomere probe (CCCTAA repeats) C-rich / leading strand Reacts to human, mouse, rat, etc |
| F1002 | TelC-Cy3 | Cy3 | |
| F1003 | TelC-Cy5 | Cy5 | |
| F1004 | TelC-Alexa488 | Alexa Fluor 488 | |
| F1009 | TelC-FITC | FITC | |
| F1013 | TelC-Alexa647 | Alexa Fluor 647 | |
| F2001 | TelC-Biotin | Biotin | |
| F1005 | TelG-FAM | FAM | TelG telomere probe (TTAGGG repeats) G-rich / lagging strand Reacts to human, mouse, rat, etc |
| F1006 | TelG-Cy3 | Cy3 | |
| F1007 | TelG-Cy5 | Cy5 | |
| F1008 | TelG-Alexa488 | Alexa Fluor 488 | |
| F1010 | TelG-FITC | FITC | |
| F1014 | TelG-Alexa 647 | Alexa Fluor 647 | |
| F2002 | TelG-Biotin | Biotin | |
| F3001 | CENPB-FAM | FAM | Pan-centromere probe (ATTCGTTGGAAACGGGA) Reacts to human & mouse |
| F3002 | CENPB-Cy3 | Cy3 | |
| F3004 | CENPB-Alexa488 | Alexa Fluor 488 | |
| F3005 | CENPB-Cy5 | Cy5 | |
| F3008 | CENPB-Biotin | Biotin | |
| F3009 | CENPB-RC-Cy3 | Cy3 | |
| F3010 | CENPB-FITC | FITC | |
| F3011 | CENPB-Alexa647 | Alexa Fluor 647 | |
| F3003 | CENT-Cy3 | Cy3 | Human only pan-centromere probe (AAACTAGACAGAAGCATT) |
| F3006 | CENT-FAM | FAM | |
| F3007 | CENT-RC-A488 | Alexa488 | |
| F5001 | (CAG)5-Cy3 | Cy3 | Stains CAG repeats (DM-1) |
| F5002 | (CAG)5-Cy5 | Cy5 | |
- Cy3 is more stable alternative for Texas Red, TRITC, TMR and other red dyes.
- Visualization of the three-dimensional structure of the human centromere in mitotic chromosomes by superresolution microscopy. Tommaso ED et al. (2023) Mol Biol Cell 34(6): ar61.
- Adjusting the Structure of a Peptide Nucleic Acid (PNA) Molecular Beacon and Promoting Its DNA Detection by a Hybrid with Quencher-Modified DNA. Hajime H et al. (2022) Processes 10(4):722.
- Fluorescence spectroscopic detection and measurement of single telomere molecules. Beh CW et al. (2018) Nucleic Acids Res 46(19): e117.
- Integrity of the human centromere DNA repeats is protected by CENP-A, CENP-C, & CENP-T . Giunta S & Funabiki H. (2017) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114(8):1928-1933.
- Comprehensive characterization of neutrophil genome topology. Zhu Y et al. (2017) Genes & Development. 31(2):141–153.
- Long telomeres protect against age-dependent cardiac disease caused by NOTCH1 haploinsufficiency. Theodoris CV et al. (2017) J Clinical Investigation 127(5):1683-1688.
- Quantification of telomere features in tumor tissue sections by an automated 3D imaging-based workflow. Gunkel M et al (2017) Methods 114:60-73.
- Telomere Replication Stress Induced by POT1 Inactivation Accelerates Tumorigenesis. Pinzaru AM et al. (2016) Cell Rep 15(10):2170-2184.
- Regulation of the Human Telomerase Gene TERT by Telomere Position Effect—Over Long Distances (TPE-OLD): Implications for Aging and Cancer. Kim W et al (2016) pLoS Biology 2000016.
- Dysfunctional telomeres induce p53‐dependent and independent apoptosis to compromise cellular proliferation and inhibit tumor formation. Wang Y et al (2016) Aging Cell 15(4): 646–660.
- ATRX loss promotes tumor growth and impairs nonhomologous end joining DNA repair in glioma. Koschmann C et al (2016) Sci Transl Med. 8(328):328.
- Oocyte Polarization Is Coupled to the Chromosomal Bouquet, a Conserved Polarized Nuclear Configuration in Meiosis. Elkouby YM et al. (2016) PLoS Biol. 14(1):e1002335.
- Cell Death During Crisis Is Mediated by Mitotic Telomere Deprotection. Hayashi MT et al (2015)Nature 522(7557):492–496.
- SMARCAL1 maintains telomere integrity during DNA replication. Poole LA et al. (2015) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 112(48):14864-14869.
- Visualization and quantitative analysis of extrachromosomal telomere-repeat DNA in individual human cells by Halo-FISH. Komosa M et al. (2015)Nucleic Acids Res. 43(4):2152–2163.
- Flap Endonuclease 1 Limits Telomere Fragility on the Leading Strand.Teasley DC et al (2015) J Biol Chem. 290(24):15133-45.
- Replication Stress and Telomere Dysfunction Are Present in Cultured Human Embryonic Stem Cells. Janson C et al (2015) Cytogenet Genome Res. 146(4):251-60.
- Genomic mosaicism with increased amyloid precursor protein (APP) gene copy number in single neurons from sporadic Alzheimer’s disease brains. Bushman DM et al. (2015) Elife 4:e05116.
- Somatic mosaicism of EPAS1 mutations in the syndrome of paraganglioma and somatostatinoma associated with polycythemia. Yang C et al (2015) Hum Genome Var. 2:15053.
- Induction of telomere dysfunction mediated by the telomerase substrate precursor 6-thio-2′-deoxyguanosine. Mender I et al (2015) Cancer Discov. 5(1):82-95.
- Role of Tet proteins in enhancer activity and telomere elongation. Lu F et al (2014)Genes Dev. 28(19): 2103–2119.
- Expression of the genetic suppressor element 24.2 (GSE24.2) decreases DNA damage andoxidative stress in X-linked dyskeratosis congenita cells. Manguan-Garcia C et al. (2014) PLoS One. 9(7):e101424.
- Telomerase Protects Werner Syndrome Lineage-Specific Stem Cells from Premature Aging. Cheung HH et al (2014) Stem Cell Reports 2(4):534–546.
- Rapid analysis of chromosome aberrations in mouse B lymphocytes by PNA-FISH. Misenko SM & Bunting SF (2014) Journal of visualized experiments 10.3791/51806.
- Identification of small juvenile stem cells in aged bone marrow and their therapeutic potential for repair of the ischemic heart. Igura K et al (2013) Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 305(9): H1354–H1362.
- Structure of the human telomeric Stn1-Ten1 capping complex. Bryan C et al (2013) PLoS One 8(6):e66756.
- Direct DNA and PNA probe binding to telomeric regions without classical in situ hybridization. Genet MD et al (2013) Molecular Cytogenetics 6:42.
- Telomere and microtubule targeting in treatment-sensitive and treatment-resistant human prostate cancer cells. Zhang B et al (2012) Mol Pharmacol. 82(2):310-321.
- Assessing telomeric DNA content in pediatric cancers using whole-genome sequencing data. Parker M et al (2012) Genome Biol. 13(12):R113.
- Dynamic rearrangement of telomeres during spermatogenesis in mice. Tanemura K et al. (2005) Dev Bio 281:196-207.
- High-throughput telomere length quantification by FISH and its application to human population studies. Canela A et al (2007) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(13):5300-5. (Q-FISH)
- Analysis of repetitive DNA in chromosomes by flow cytometry. Brind-Amour J and Lansdorp PM (2011) Nat Methods 8(6):484-6.(Q-FISH & Flow FISH)
- Age-related telomere length dynamics in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of healthy cynomolgus monkeys measured by Flow FISH. Lee WW et al (2002) Immunology 105:458-65. (Q-FISH & Flow FISH)
- Single base discrimination of CENP-B repeats on mouse and human Chromosomes with PNA-FISH. Chen C et al (1999) Mammalian Genome 10(1):13–18.
FISH probes and reagents are usually in stock and shipped out the same day for the next day delivery if the order is received by 5 pm EST.
| Cat No | Item | Description | Size | Price | Order |
| F1001 | TelC-FAM | C-rich telomere probe, FAM labeled | 5 nmole | $295.00 | Add to cart |
| F1002 | TelC-Cy3 | C-rich telomere probe, Cy3 labeled | 5 nmole | $295.00 | Add to cart |
| F1003 | TelC-Cy5 | C-rich telomere probe, Cy5 labeled | 5 nmole | $295.00 | Add to cart |
| F1004 | TelC-Alexa488 | C-rich telomere probe, Alexa Fluor 488 labeled | 5 nmole | $375.00 | Add to cart |
| F1005 | TelG-FAM | G-rich telomere probe, FAM labeled | 5 nmole | $295.00 | Add to cart |
| F1006 | TelG-Cy3 | G-rich telomere probe, Cy3 labeled | 5 nmole | $295.00 | Add to cart |
| F1007 | TelG-Cy5 | G-rich telomere probe, Cy5 labeled | 5 nmole | $295.00 | Add to cart |
| F1008 | TelG-Alexa488 | G-rich telomere probe, Alexa Fluor 488 labeled | 5 nmole | $375.00 | Add to cart |
| F1009 | TelC-FITC | C-rich telomere probe, FITC labeled | 5 nmole | $295.00 | Add to cart |
| F1010 | TelG-FITC | G-rich telomere probe, Cy3 labeled | 5 nmole | $295.00 | Add to cart |
| F1013 | TelC-Alexa647 | C-rich telomere probe, Alexa Fluor 647 labeled | 5 nmole | $375.00 | Add to cart |
| F1014 | TelG-Alexa647 | G-rich telomere probe, Alexa Fluor 647 labeled | 5 nmole | $375.00 | Add to cart |
| F1015 | TelC-TexasRed | C-rich telomere probe, Texas Red labeled | 5 nmole | $295.00 | Add to cart |
| F2001 | TelC-Biotin | C-rich telomere probe, Biotin labeled | 5 nmole | $295.00 | Add to cart |
| F2002 | TelG-Biotin | G-rich telomere probe, Biotin labeled | 5 nmole | $295.00 | Add to cart |
| F3001 | CENPB-FAM | CENP-B box binding pan-centromere probe, FAM labeled | 5 nmole | $295.00 | Add to cart |
| F3010 | CENPB-FITC | CENP-B box binding pan-centromere probe, FITC labeled | 5 nmole | $295.00 | Add to cart |
| F3002 | CENPB-Cy3 | CENP-B box binding pan-centromere probe, Cy3 labeled | 5 nmole | $295.00 | Add to cart |
| F3004 | CENPB-Alexa488 | CENP-B box binding pan-centromere probe, Alexa Fluor 488 labeled | 5 nmole | $375.00 | Add to cart |
| F3005 | CENPB-Cy5 | CENP-B box binding pan-centromere probe, Cy5 labeled | 5 nmole | $295.00 | Add to cart |
| F3011 | CENPB-Alexa647 | CENP-B box binding pan-centromere probe, Alexa Fluor 647 labeled | 5 nmole | $375.00 | Add to cart |
| F3008 | CENPB-Biotin | CENP-B box binding pan-centromere probe, Biotin labeled | 5 nmole | $295.00 | Add to cart |
| F3009 | CENPBR-Cy3 | Reverse complement of CENPB probe, Cy3 labeled | 5 nmole | $295.00 | Add to cart |
| F3003 | CENT-Cy3 | Centromere probe, Cy3 labeled | 5 nmole | $295.00 | Add to cart |
| F3006 | CENT-FAM | Centromere probe, FAM labeled | 5 nmole | $295.00 | Add to cart |
| F3007 | CENT-RC-A488 | Reverse complement of CENT probe, Alexa488 labeled | 5 nmole | $375.00 | Add to cart |
| F5001 | (CAG)5-Cy3 | CAG repeats, Cy3 labeled | 5 nmole | $295.00 | Add to cart |
| F5002 | (CAG)-Cy5 | CAG repeats, Cy5 labeled | 5 nmole | $295.00 | Add to cart |
| PFB01 | Hybridization Buffer | PNA FISH Hybridization Buffer | 30 ml | $55.00 | Add to cart |
| PFB05 | FISH Blocking Buffer | PNA FISH Blocking Reagent | 1.5 ml | $25.00 | Add to cart |